Diagnosis
Psychometric tests
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) represents a continuum of neuropsychiatric changes and altered consciousness. Progression of covert HE (CHE) to overt HE (OHE) and its impact of quality of life make its early diagnosis imperative. Despite the availability of several diagnostic techniques ranging from simple clinical scales to sophisticated computerised tests, diagnosis remains a challenge due to the time, cost and personnel involved. Psychometric tests therefore appear promising due to their high sensitivity and low cost, but results are variable depending on age and education.1
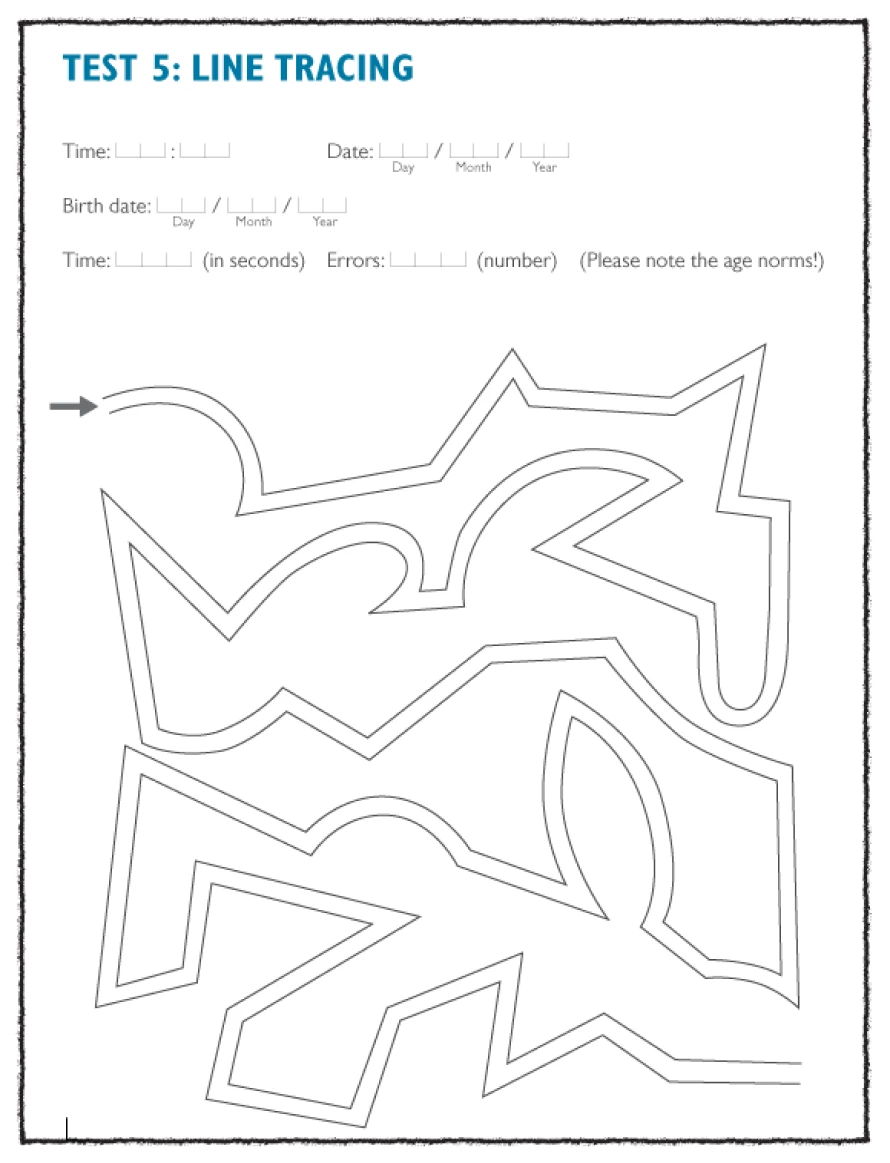
Well-validated and easily quantifiable psychometric test procedures, which determine deficits in psychomotor performance speed and visual constructive ability, are the number connection test (NCT), versions A and B, the digit symbol test, the serial dotting test, and the line tracing test. These tests are simple to explain to the patient, quick to perform, and easy to evaluate.1
The portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE) syndrome test is a standardised assessment tool especially useful for the diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE) that collects the number connection test, the digit symbol test, and the line tracing test, and adds the pointing in the circle test.1
The recently developed EncephalApp-Stroop is a high-sensitivity test to screen for covert HE and meets the need for a brief screening tool for covert HE that does do not require psychological expertise in administration and interpretation.1
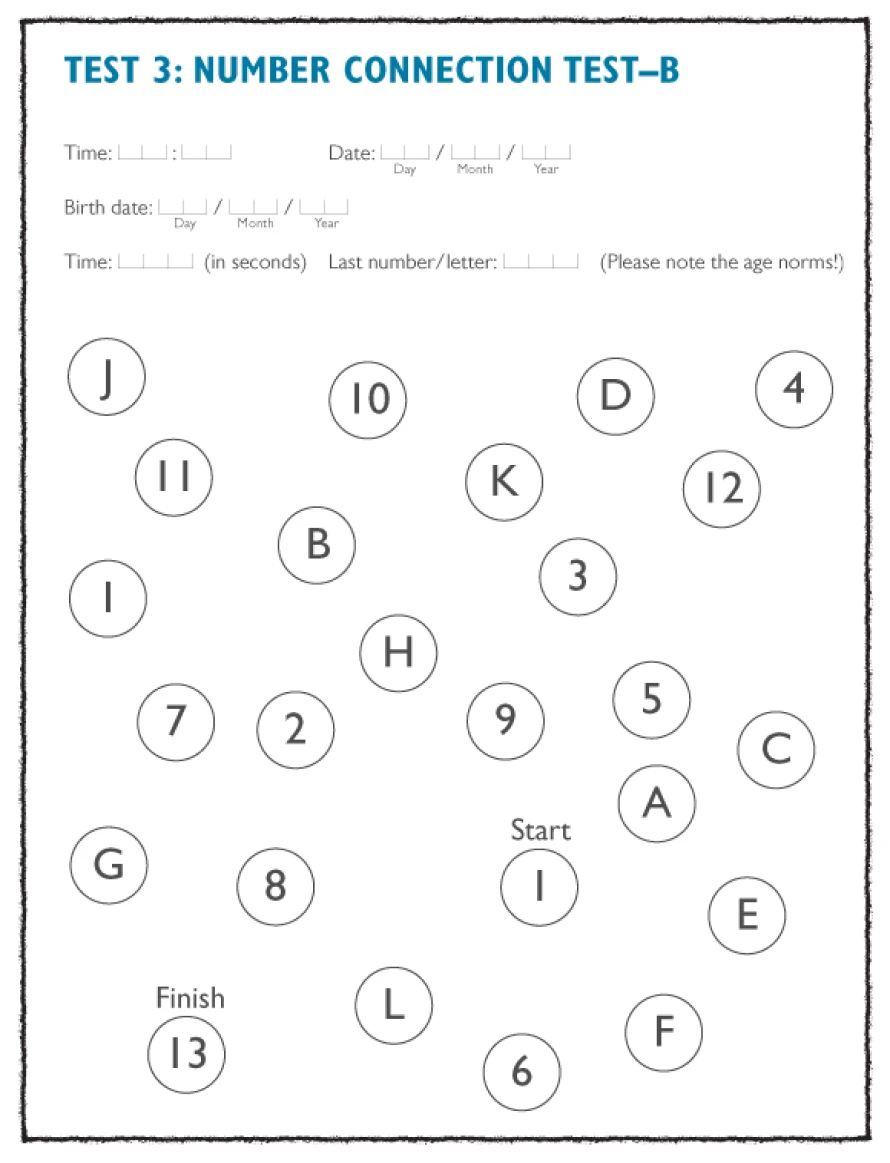
Number connection test, versions A (NCT-A) and B (NCT-B)
In NCT-A the numbers have to be joined consecutively in ascending numerical order (1, 2, 3…) as quickly as possible. In the more complicated NCT-B, the numbers and letters must be connected alternately numerically and alphabetically (1, A, 2, B…). Evaluation of both tests is based on the time required to complete the test.2

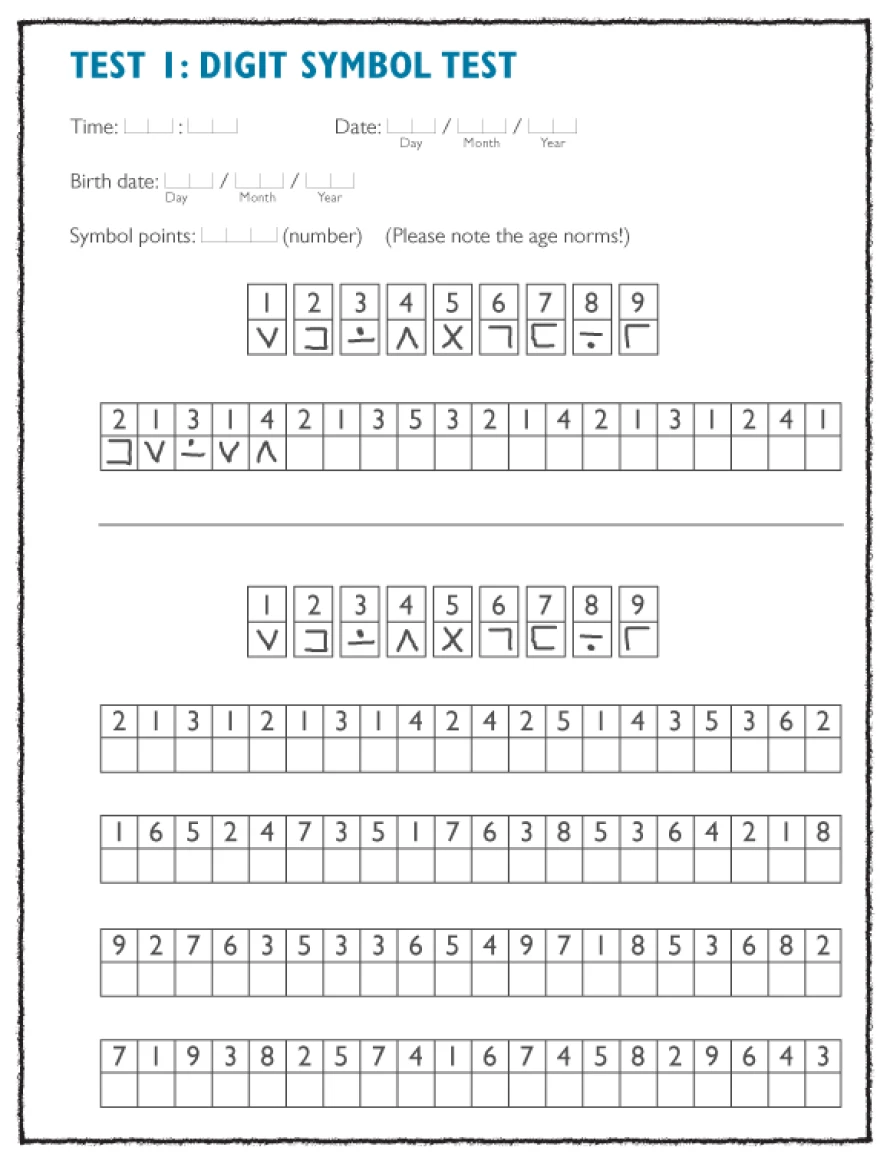
Digit-symbol test and the tracking test, examples of psychometric tests which can be used as a diagnostic tool in patients with suspected HE
Psychometric tests are simple to administer and appropriate for the diagnosis of minimal HE and HE.1
Disadvantages: learning effects, strong emphasis on fine motor skills
Using EncephalApp-Stroop
EncephalApp-Stroop is a high-sensitivity test to screen for covert HE and meets the need for a brief screening tool for covert HE that does do not require psychological expertise in administration and interpretation. Stroop tasks have been used for a long time to evaluate psychomotor speed and cognitive flexibility. They are now available as a new Smartphone app that is available on iTunes. The most recent of these, the EncephalApp-Stroop app, is free to download. The age-based cut-offs for EncephalApp-Stroop are highly sensitive for covert HE screening and could be used to guide future dedicated testing in cirrhosis. The app has good discriminative validity and good test-retest reliability. It is easy to perform and administer (being patient-controlled) and within 5 min is able to give >88% sensitivity for the diagnosis of MHE and cognitive dysfunction in cirrhosis.1
EncephalApp-Stroop features and functionality1
EncephalApp is a series of applications designed to evaluate patients with liver disease; the first of which is a Stroop task.
It has neutral and incongruent stimuli only.
Stroop “Off” state No words, just symbols
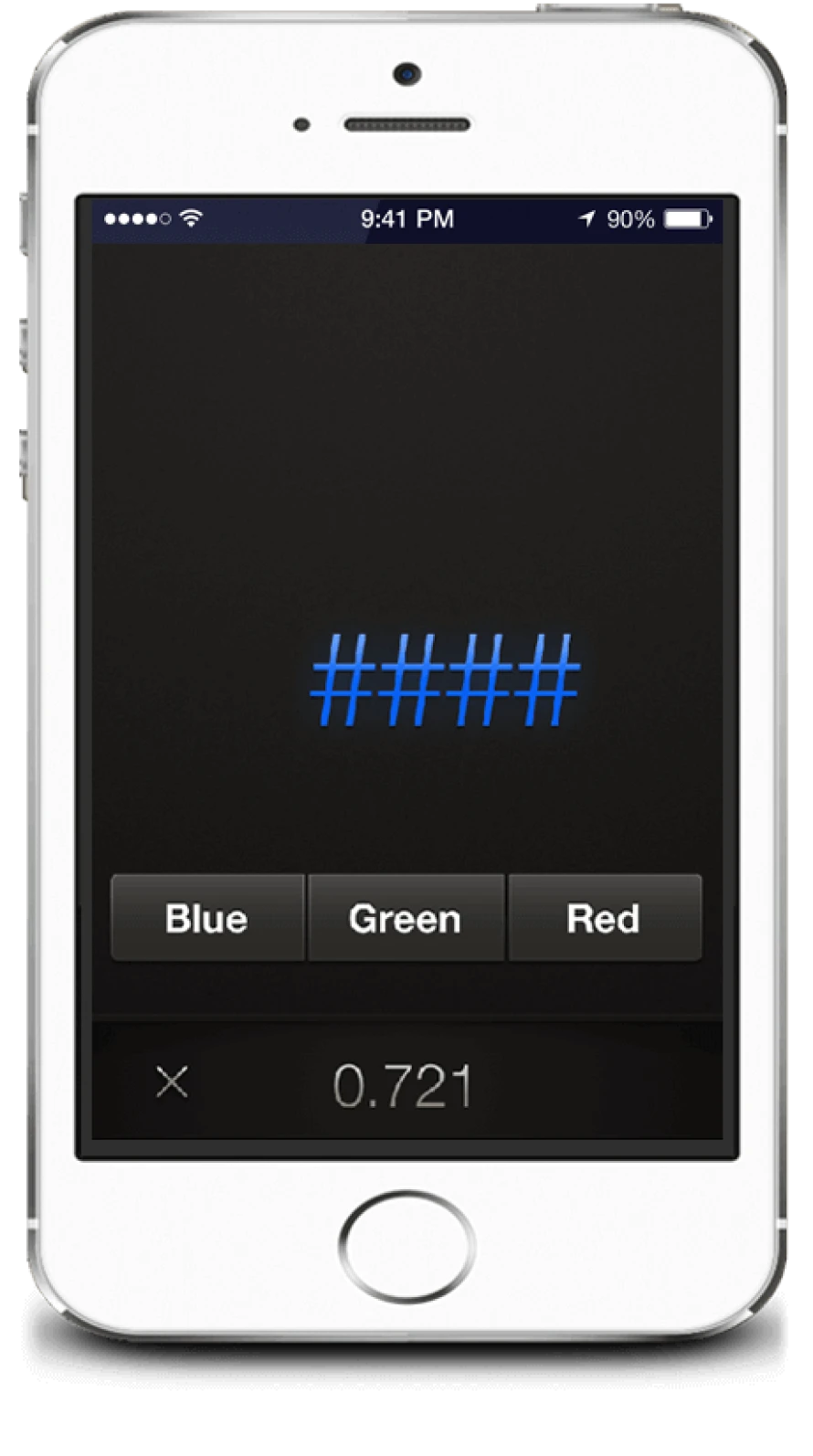
The task is to correctly and rapidly press the colour corresponding to the colour of the symbols presented.
Stroop “On” state Words in discordant colours
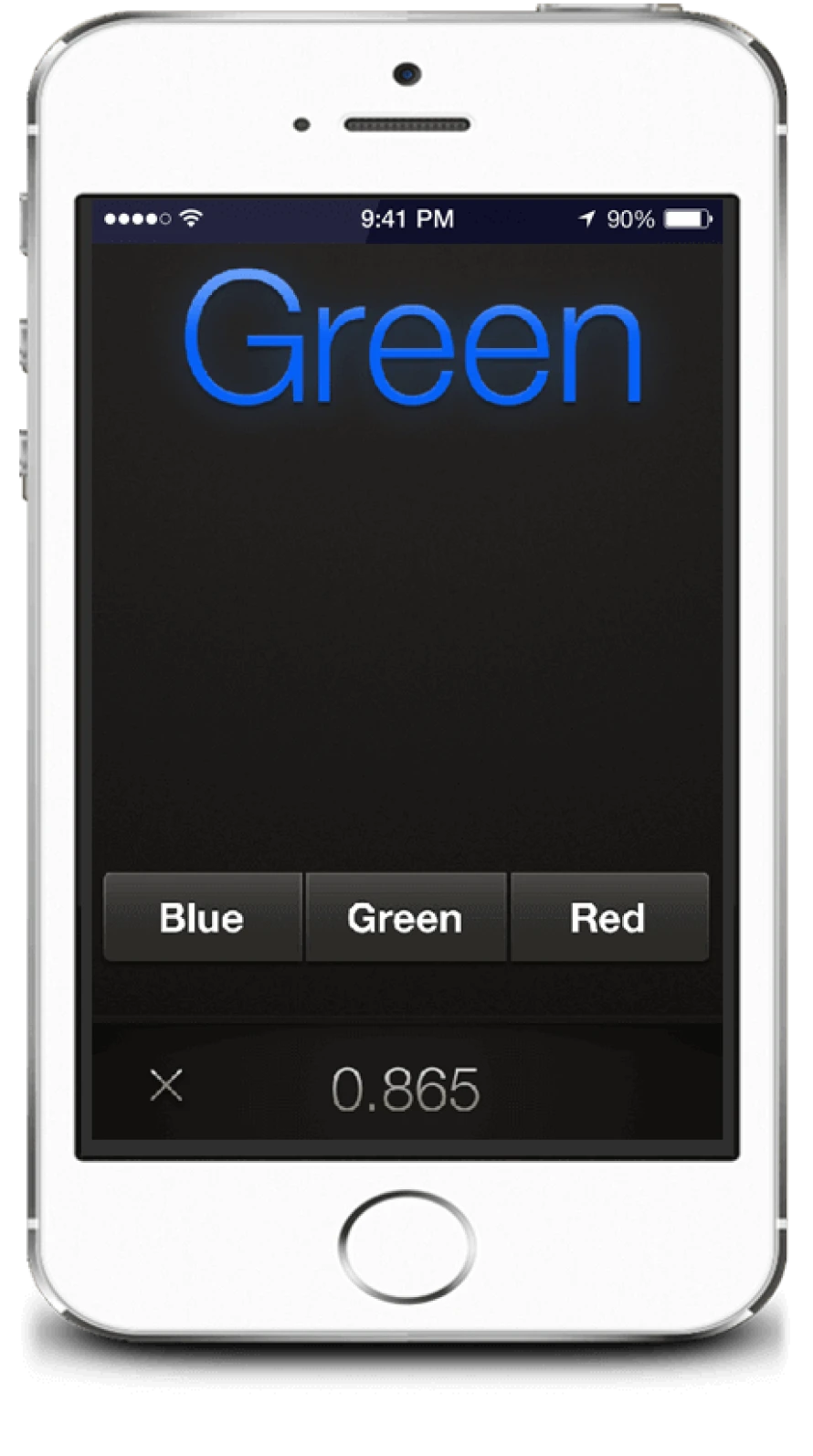
The task is to correctly and rapidly press the colour corresponding to the colour of the word presented, not the colour it means.
Stroop outputs
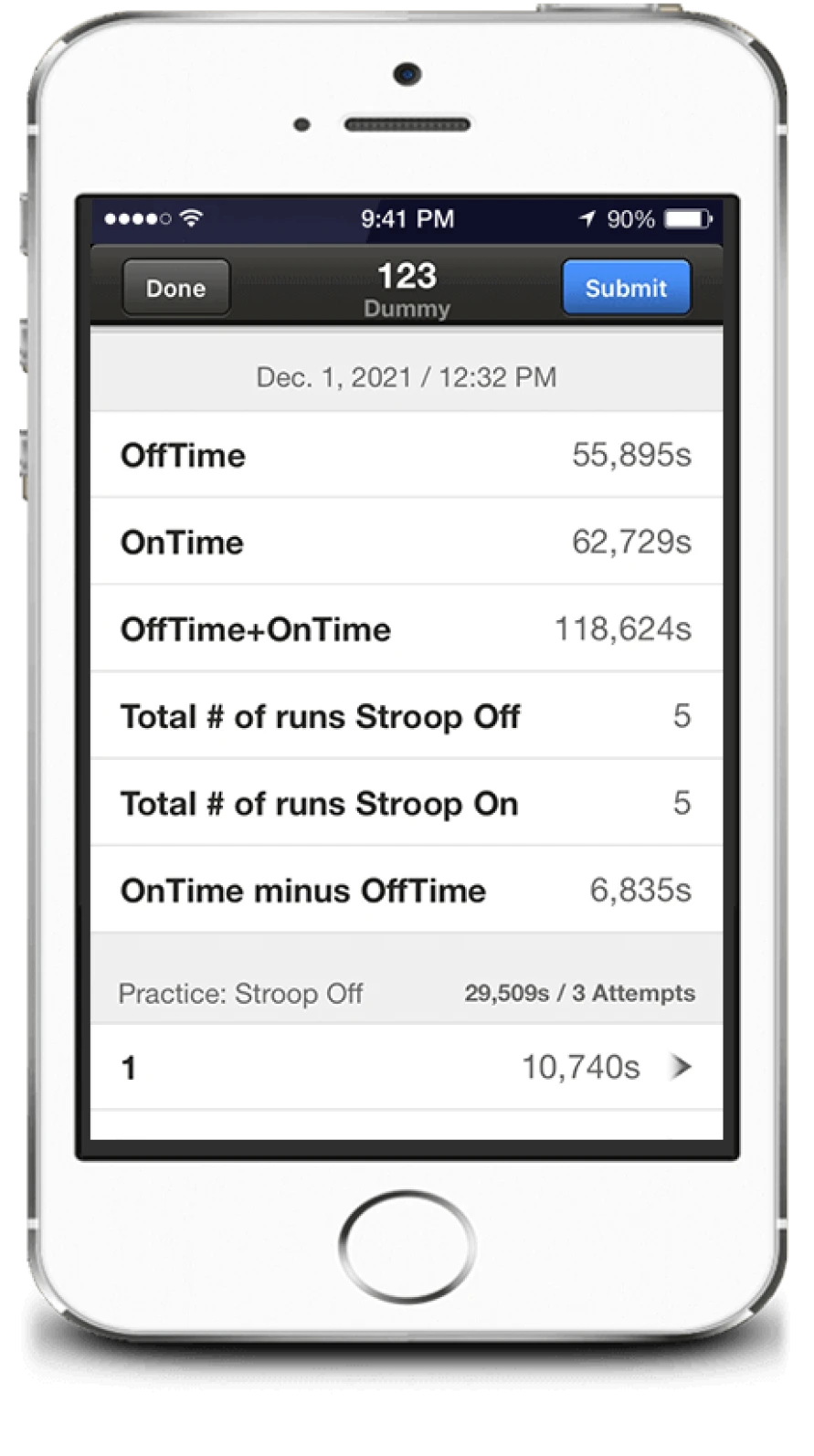
- Each run has 10 stimuli
- One mistake stops it
- 5 complete runs in off and on state are needed
- Outputs in “on” and “off” state:
- Number of runs needed to achieve 5 correct runs
- Time needed to complete those 5 correct runs
1. Nabi E, Bajaj JS. Useful tests for hepatic encephalopathy in clinical practice. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2014;16(1):362.
2. Weissenborn K et al. Neuropsychological characterization of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol. 2001;34:768-773.